
Kabuki syndrome A new case associated with Becker nevus
4 min read. Kabuki syndrome (KS) is a rare condition that affects multiple parts of the body. The name comes from the facial features typical of those with the disorder. They often have high.

FileChild with Kabuki Syndrome 04.jpg Wikimedia Commons
Introduction. Kabuki syndrome (KS, OMIM # 147920 and 300867) was firstly described by Niikawa and Kuroki [1-3] and, over the years, has become a well-recognized multiple congenital anomaly/intellectual disability (ID) disorder.The incidence of KS is about 1/32,000 of live births [].The lysine (K)-specific methyltransferase 2 family (KMT2 A-E), originally named the myeloid/lymphoid or mixed.

Kabuki syndrome causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis
Kabuki syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that occurs in around one in 32,000 births. It was first described in 1981 by scientists Norio Niikawa and Yoshikazu Kuroki who observed several children with similar characteristics. Kabuki syndrome is also known as KMS or Niikawa-Kuroki syndrome. Children with Kabuki syndrome may have a number of.

The Most Important Thing I’ve Learned Since My Daughter Was Diagnosed With Kabuki Syndrome
Kabuki syndrome is a rare, multisystem disorder characterized by multiple abnormalities including distinctive facial features, growth delays, varying degrees of intellectual disability, skeletal abnormalities and short stature. A wide variety of additional symptoms affecting multiple different organ systems can potentially occur.

The patient shows the typical facial features of Kabuki syndrome, such... Download Scientific
Kabuki syndrome. Kabuki syndrome (also previously known as Kabuki-makeup syndrome (KMS) or Niikawa-Kuroki syndrome) is a congenital disorder of genetic origin. [1] [2] It affects multiple parts of the body, with varying symptoms and severity, although the most common is the characteristic facial appearance. [3]

Facial features of Kabuki syndrome patients . Representative images of... Download Scientific
Kabuki-Syndrom. Das Kabuki-Syndrom (früher auch Niikawa-Kuroki-Syndrom oder Kabuki-Make-up-Syndrom genannt) ist eine sehr seltene angeborene Krankheit, welche aus einem Gendefekt resultiert. [1] Der Name leitet sich von Kabuki, einer traditionellen japanischen Form des Theaters, ab, da die betroffenen Patienten spezielle Gesichtsmerkmale.

kabuki syndrome Syndrome, Nursing school, Kabuki
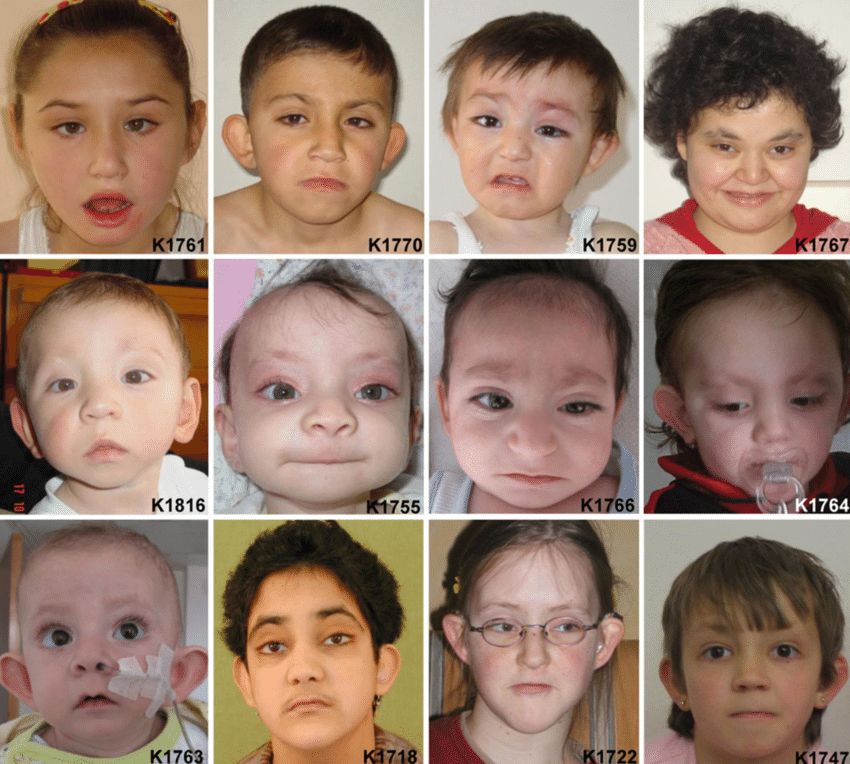
Kabuki syndrome (KS) (OMIM 147920 and OMIM 300867) is a rare genetic disorder (1 in 32,000 births) with five cardinal features: characteristic facial features, dermatoglyphic abnormalities, skeletal malformations, mild to moderate intellectual disability and short stature. Additional features include impaired fine motor skills, susceptibility.
Síndrome de Kabuki Reporte de Caso y Revisión de la Literatura NetMD® Connect Healthcare
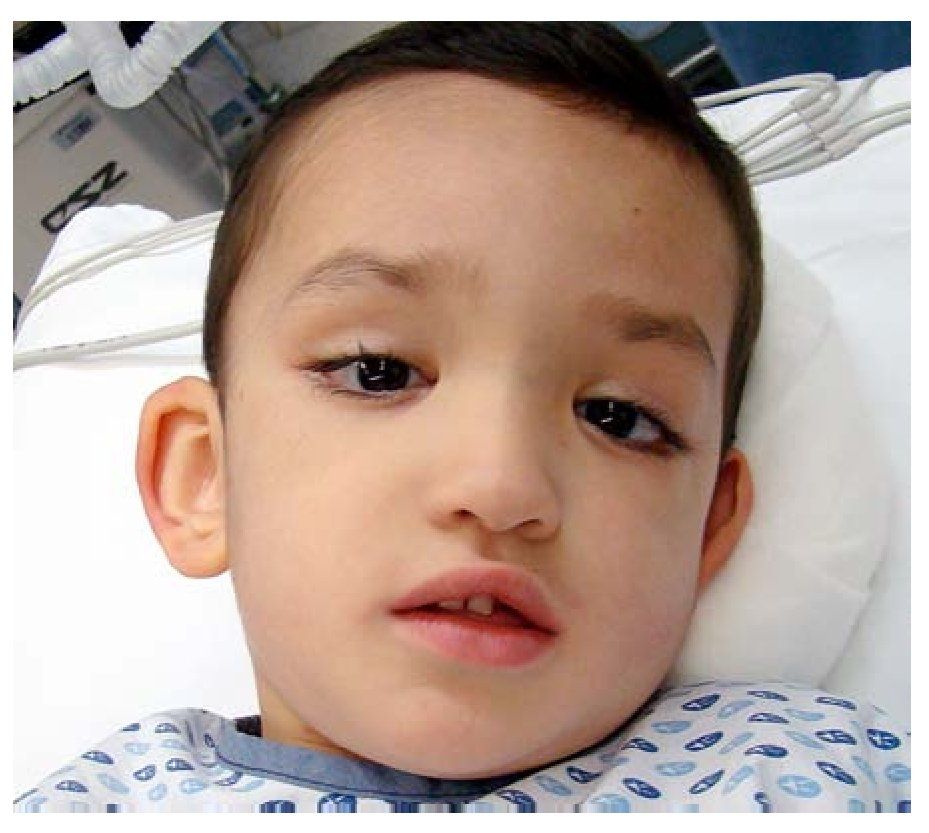
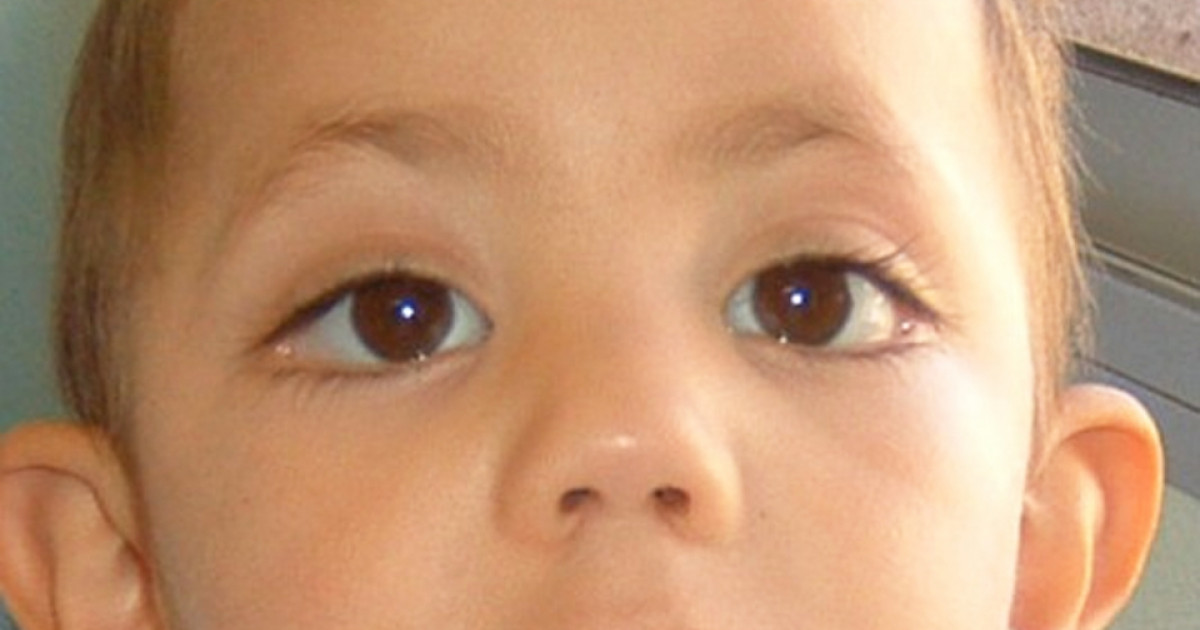
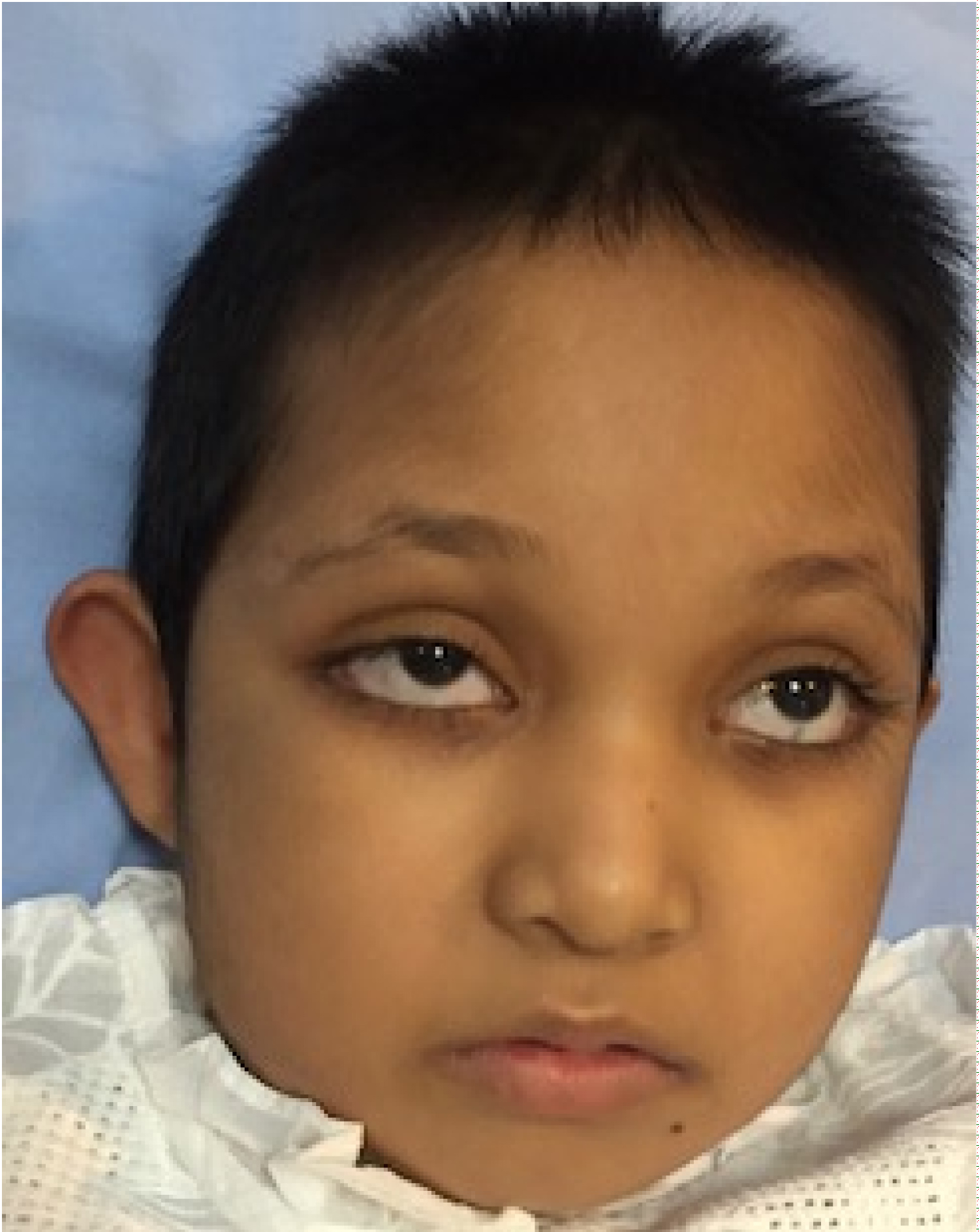
Kabuki syndrome (KS) is characterized by typical facial features (long palpebral fissures with eversion of the lateral third of the lower eyelid; arched and broad eyebrows; short columella with depressed nasal tip; large, prominent, or cupped ears), minor skeletal anomalies, persistence of fetal fingertip pads, mild-to-moderate intellectual disability, and postnatal growth deficiency. Other.
Síndrome de Kabuki síntomas, causas y tratamiento
Kabuki syndrome is a rare disorder that affects multiple parts of the body. It is present from birth. Specific symptoms and severity can vary.
Kabuki Syndrome A Rare Multisystem Disorder in Bangladesh
Kabuki syndrome (KS) is a Mendelian Disorder of the Epigenetic Machinery (MDEM) caused by loss of function variants in either of two genes involved in the regulation of histone methylation, KMT2D (34-76%) or KDM6A (9-13%). Previously, representative neurobehavioral deficits of KS were recapitulated in a mouse model, emphasizing the role of KMT2D in brain development, specifically in.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/KabukiIllustration-2210ff2d7c6348bdaed11e3abfdcfa19.jpg)
Kabuki Syndrome Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment
Most caregivers ( n = 54, 94.7%) were female and the average age of caregivers was 40 years old (range: 21-64). Caregivers reported they had both male ( n = 29, 50.9%) and female ( n = 28, 49.1%) children, with their child's age ranging from one to 32 years ( x¯ = 9). Most caregivers ( n = 54, 94.7%) reported their child was diagnosed with.
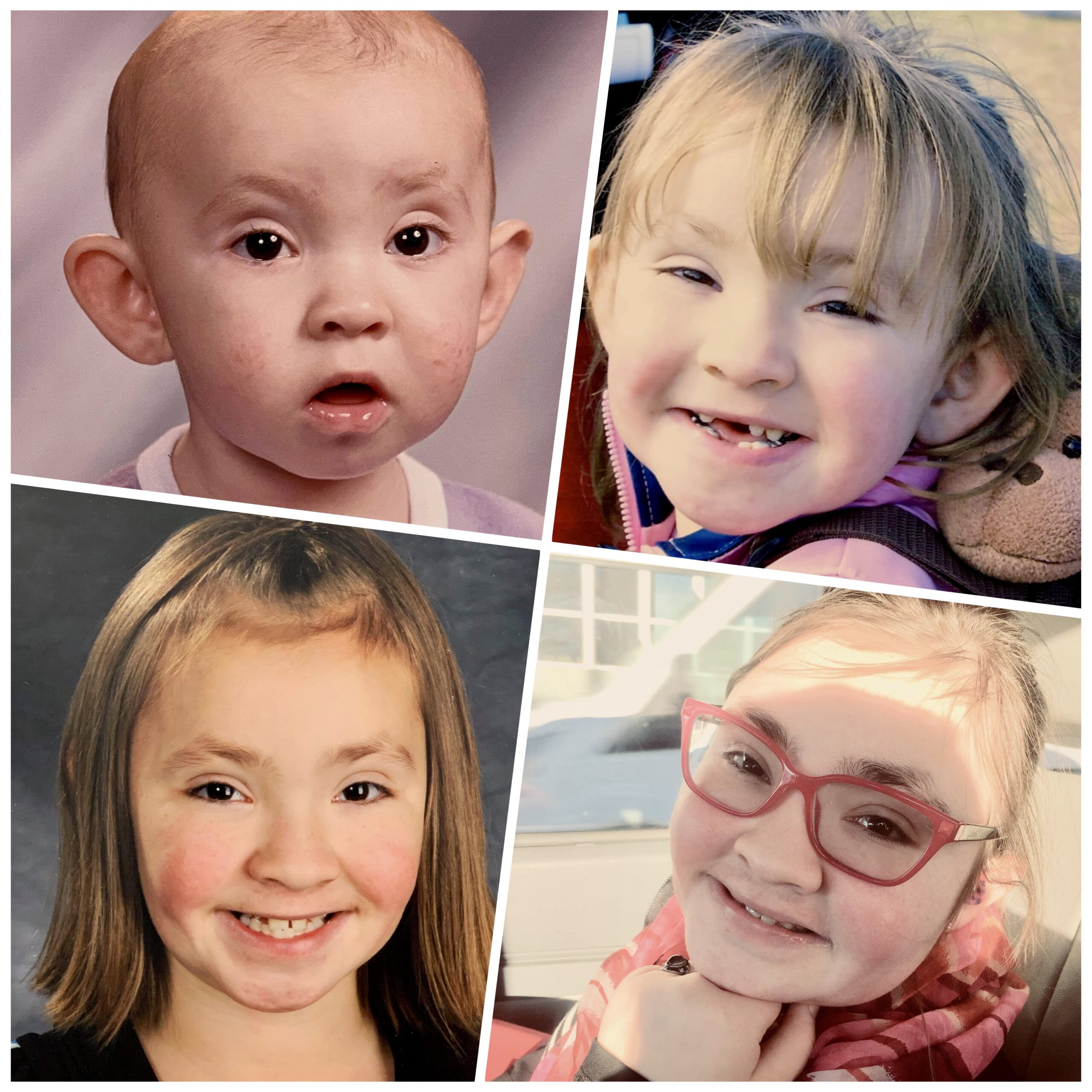

Kabuki Syndrome A Touch of Ausome
PMC is a free full-text archive of biomedical and life sciences literature at the U.S. National Institutes of Health's National Library of Medicine. This article reviews the imaging features of Kaposi sarcoma, a rare vascular tumor associated with immunosuppression, and discusses the differential diagnosis and management options.

(PDF) Kabuki Syndrome with Cleft Palate
Kabuki syndrome is a rare genetic disorder with a range of characteristics, including intellectual disability, distinctive facial features and skeletal abnormalities. Estimates suggest that Kabuki syndrome occurs in about one in every 32,000 births. However, Kabuki syndrome is thought to be underdiagnosed, so it could be more common.

Kabuki syndrome clinical and molecular diagnosis in the first year of life Archives of
Kabuki makeup syndrome (KMS) was described in Japanese children by Kuroki, Niikawa et al. in 1988. [ 1] The name comes from the makeup of actors in Japanese traditional play "Kabuki" to which the facial features resemble. A definitive diagnosis of KMS was made in the present case based on criteria laid down by International consensus.
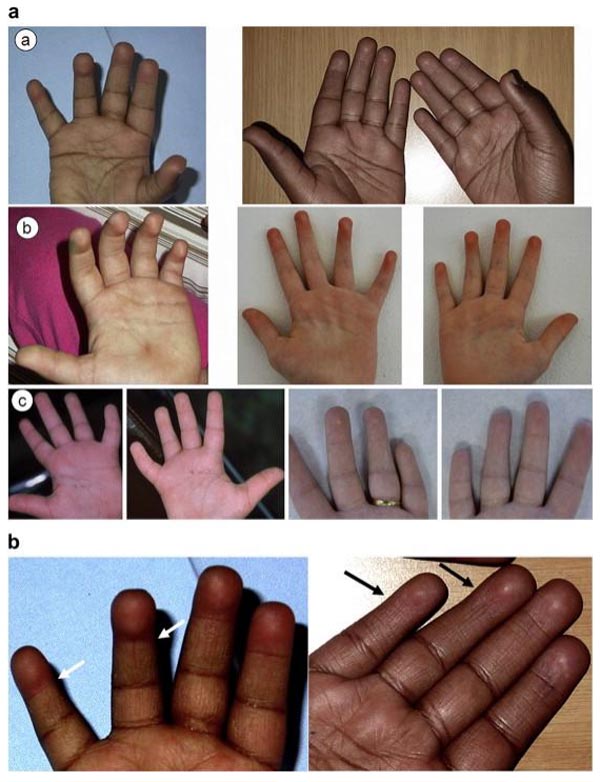
Hand Charts for Kabuki Syndrome!
Kabuki syndrome (KS) is a rare syndrome characterized by multiple congenital anomalies and mental retardation. Other characteristics include a peculiar facial gestalt, short stature, skeletal and visceral abnormalities, cardiac anomalies, and immunological defects. Whole exome sequencing has uncovered the genetic basis of KS.
Kabuki Syndrome A Touch of Ausome
Kabuki syndrome is a rare genetic syndrome that can cause various symptoms affecting various organ systems. The cause is generally related to pathogenic variations in one of two genes, KMT2D and KDM6A. Diagnosis is based on genetic testing and diagnostic criteria. Management is typically aimed toward individual needs and symptoms and requires.